Mesalazine Activates Adenosine Monophosphate-activated Protein Kinase: Implication in the Anti-inflammatory Activity of this Anti-colitic Drug | Bentham Science
Safety of 5-Aminosalicylic Acid Derivatives in Patients with Sensitivity to Acetylsalicylic Acid and Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs

Induction of Colonic Regulatory T Cells by Mesalamine by Activating the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor - ScienceDirect

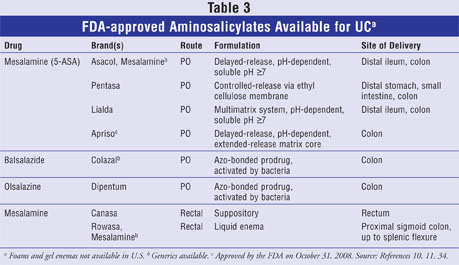
Drug Insight: aminosalicylates for the treatment of IBD | Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology

Prokinetic Drugs A gastroprokinetic agent, gastrokinetic, or prokinetic, is a type of drug which enhances gastrointestinal motility by increasing the frequency. - ppt video online download
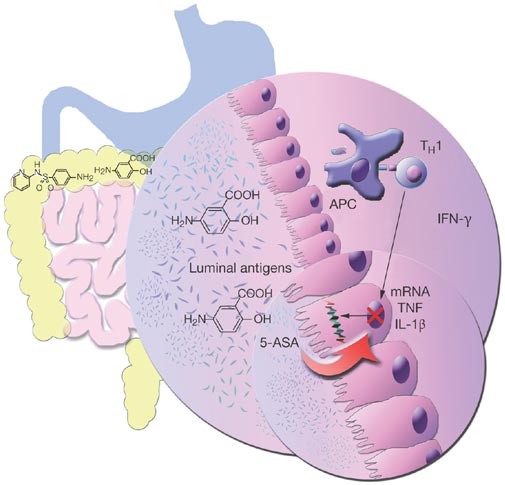
Drug Insight: aminosalicylates for the treatment of IBD | Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology

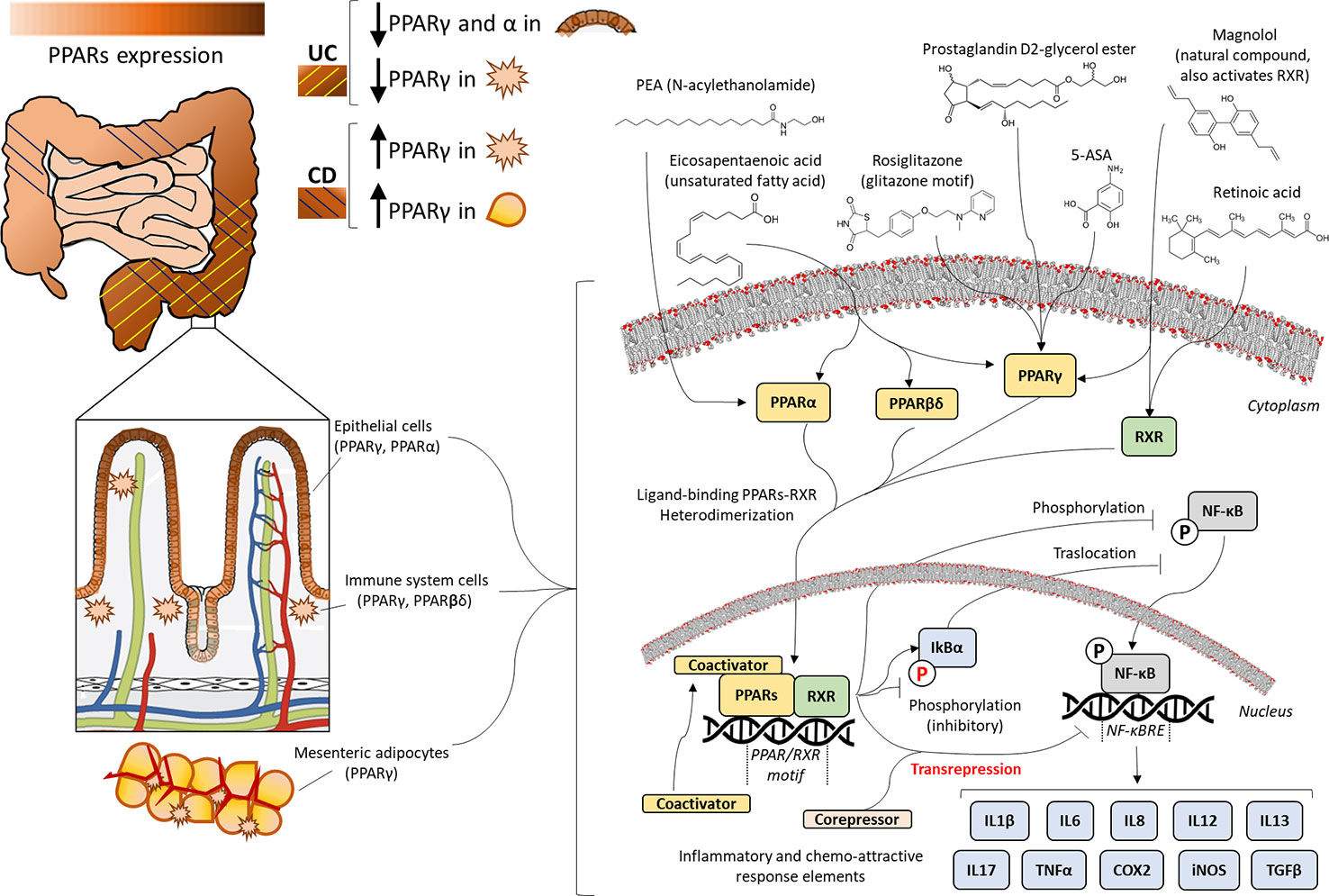
Review article: mode of action and delivery of 5‐aminosalicylic acid – new evidence - DESREUMAUX - 2006 - Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics - Wiley Online Library
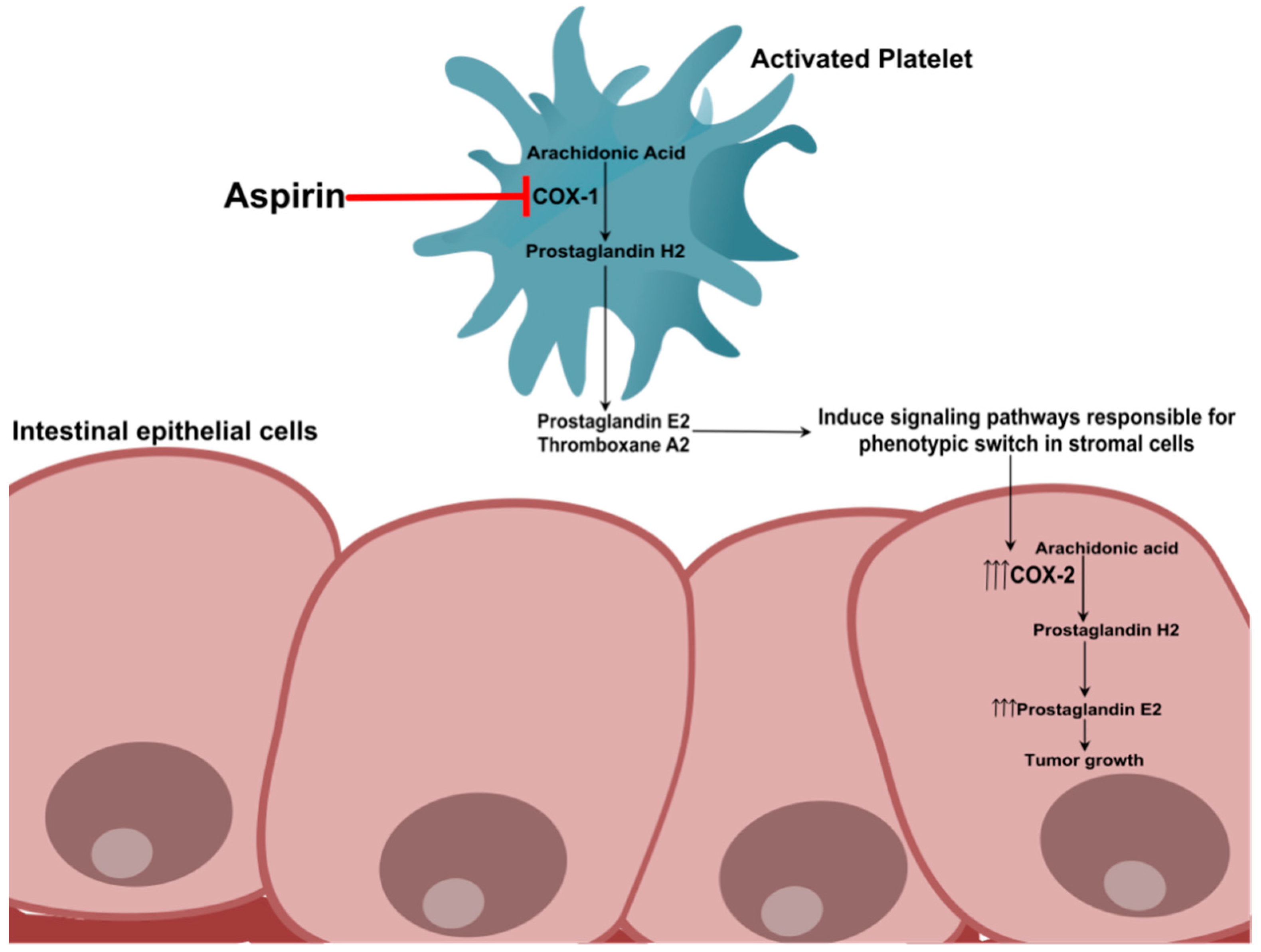
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Mechanisms of Colorectal Cancer Prevention by Aspirin—A Literature Review and Perspective on the Role of COX-Dependent and -Independent Pathways | HTML
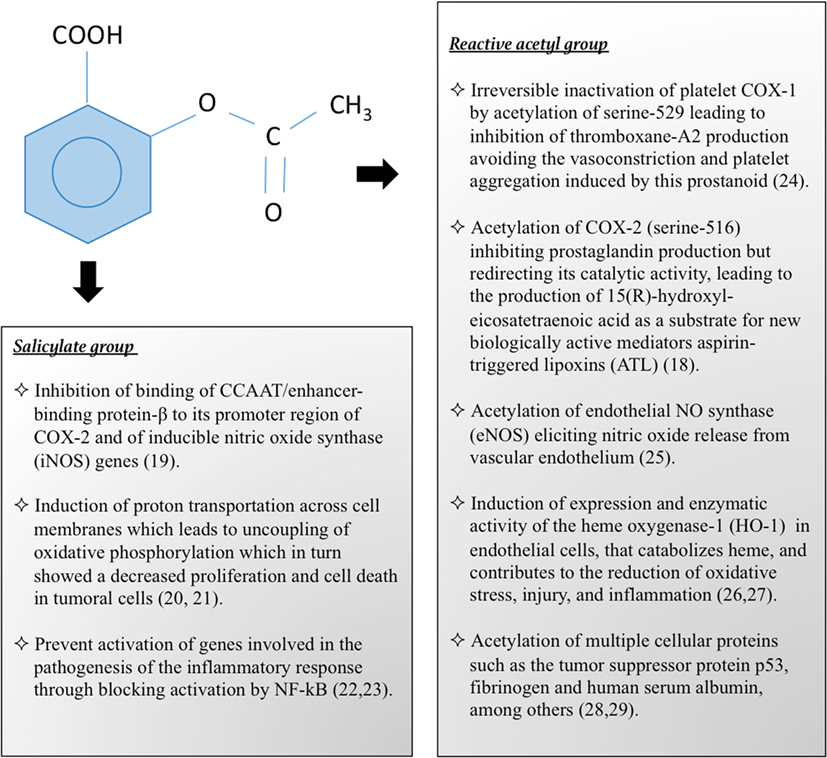
Frontiers | Aspirin: The Mechanism of Action Revisited in the Context of Pregnancy Complications | Immunology

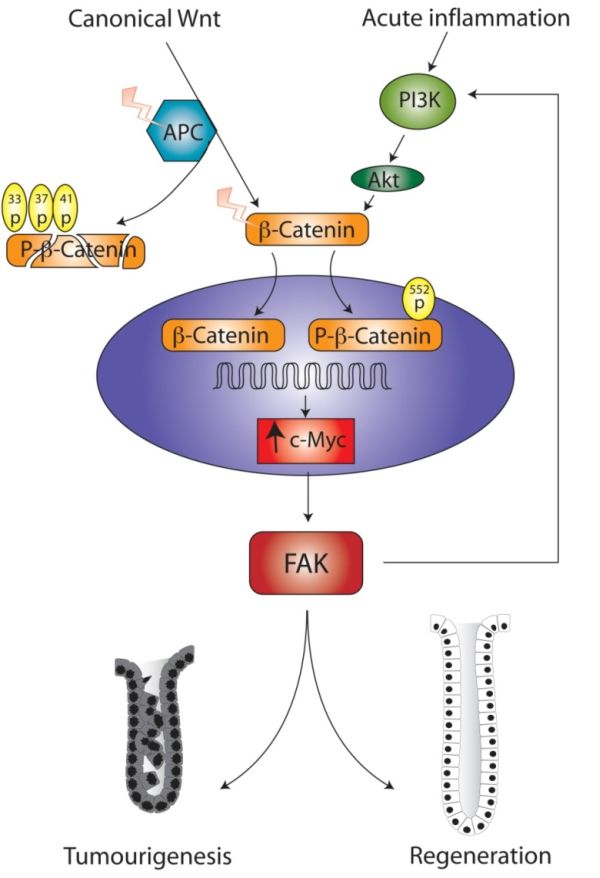
Review article: mechanisms of action of mesalazine in preventing colorectal carcinoma in inflammatory bowel disease - Allgayer - 2003 - Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics - Wiley Online Library

Mesalamine modulates intercellular adhesion through inhibition of p-21 activated kinase-1 - ScienceDirect
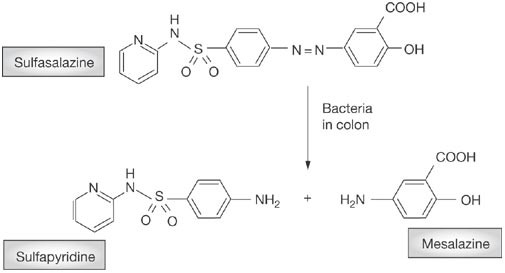
Drug Insight: aminosalicylates for the treatment of IBD | Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology

Drugs used in inflammatory bowel disease and biological and immune therapy of IBD Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit College of Medicine. - ppt download

DRUG TREATMENT OF INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. Objectives Describe the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics and adverse effects of drugs in IBD. - ppt download