
Rotenone decreases intracellular aldehyde dehydrogenase activity: implications for the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease - Goldstein - 2015 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library
PLOS ONE: Transcriptome Analysis of a Rotenone Model of Parkinsonism Reveals Complex I-Tied and -Untied Toxicity Mechanisms Common to Neurodegenerative Diseases

Paradoxical lower sensitivity of Locus Coeruleus than Substantia Nigra pars compacta neurons to acute actions of rotenone - ScienceDirect
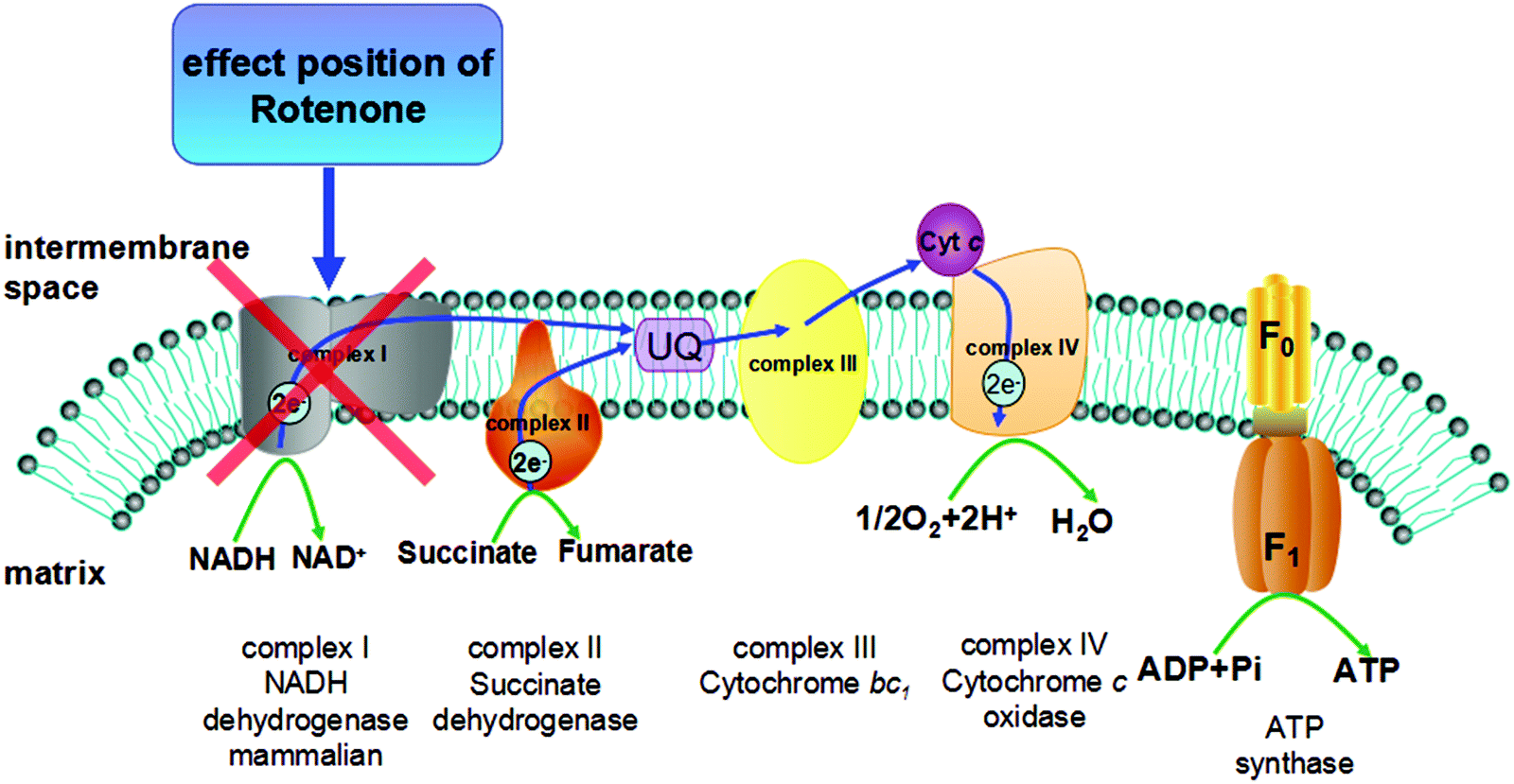
Plant species forbidden in health food and their toxic constituents, toxicology and detoxification - Food & Function (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C5FO00995B
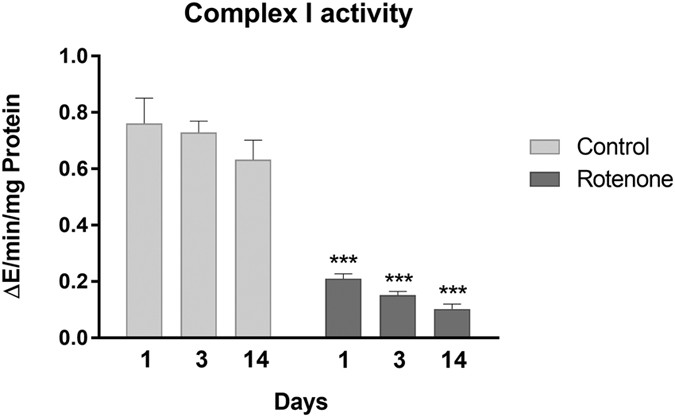
Mechanistic Investigations of the Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibitor Rotenone in the Context of Pharmacological and Safety Evaluation | Scientific Reports

Antioxidant mechanism of mitochondria-targeted plastoquinone SkQ1 is suppressed in aglycemic HepG2 cells dependent on oxidative phosphorylation - ScienceDirect
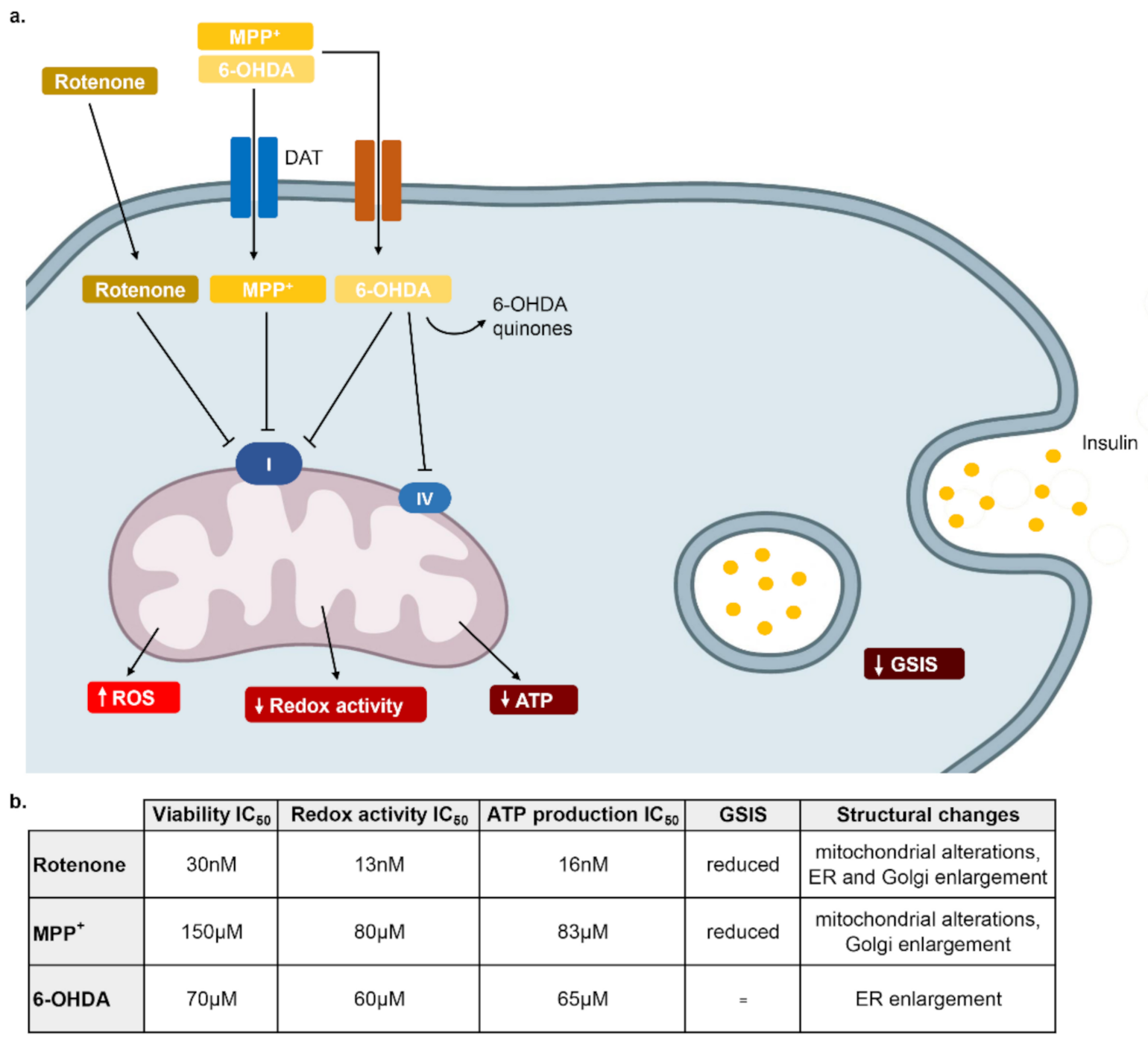
Pharmaceuticals | Free Full-Text | β-Cells Different Vulnerability to the Parkinsonian Neurotoxins Rotenone, 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) and 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) | HTML

Bioenergetic adaptation in response to autophagy regulators during rotenone exposure - Giordano - 2014 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library
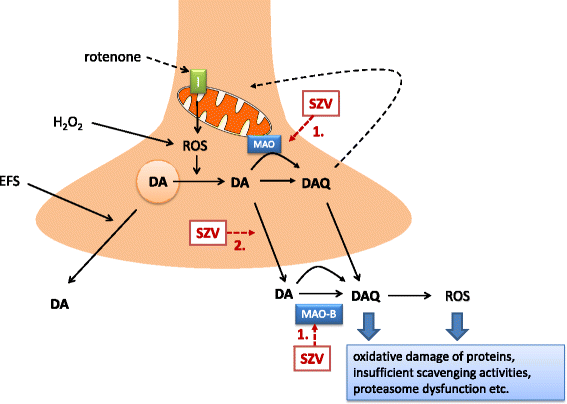
Novel (Hetero)arylalkenyl propargylamine compounds are protective in toxin-induced models of Parkinson's disease | Molecular Neurodegeneration | Full Text

Hypothetical model of rotenone-induced PD with possible therapeutic... | Download Scientific Diagram

Activation of Group III Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Attenuates Rotenone Toxicity on Dopaminergic Neurons through a Microtubule-Dependent Mechanism | Journal of Neuroscience

Rotenone Increases Isoniazid Toxicity but Does Not Cause Significant Liver Injury: Implications for the Hypothesis that Inhibition of the Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain Is a Common Mechanism of Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury.,Chemical

A schematic diagram showing how rotenone induces apoptosis by Ca 2+ /H... | Download Scientific Diagram
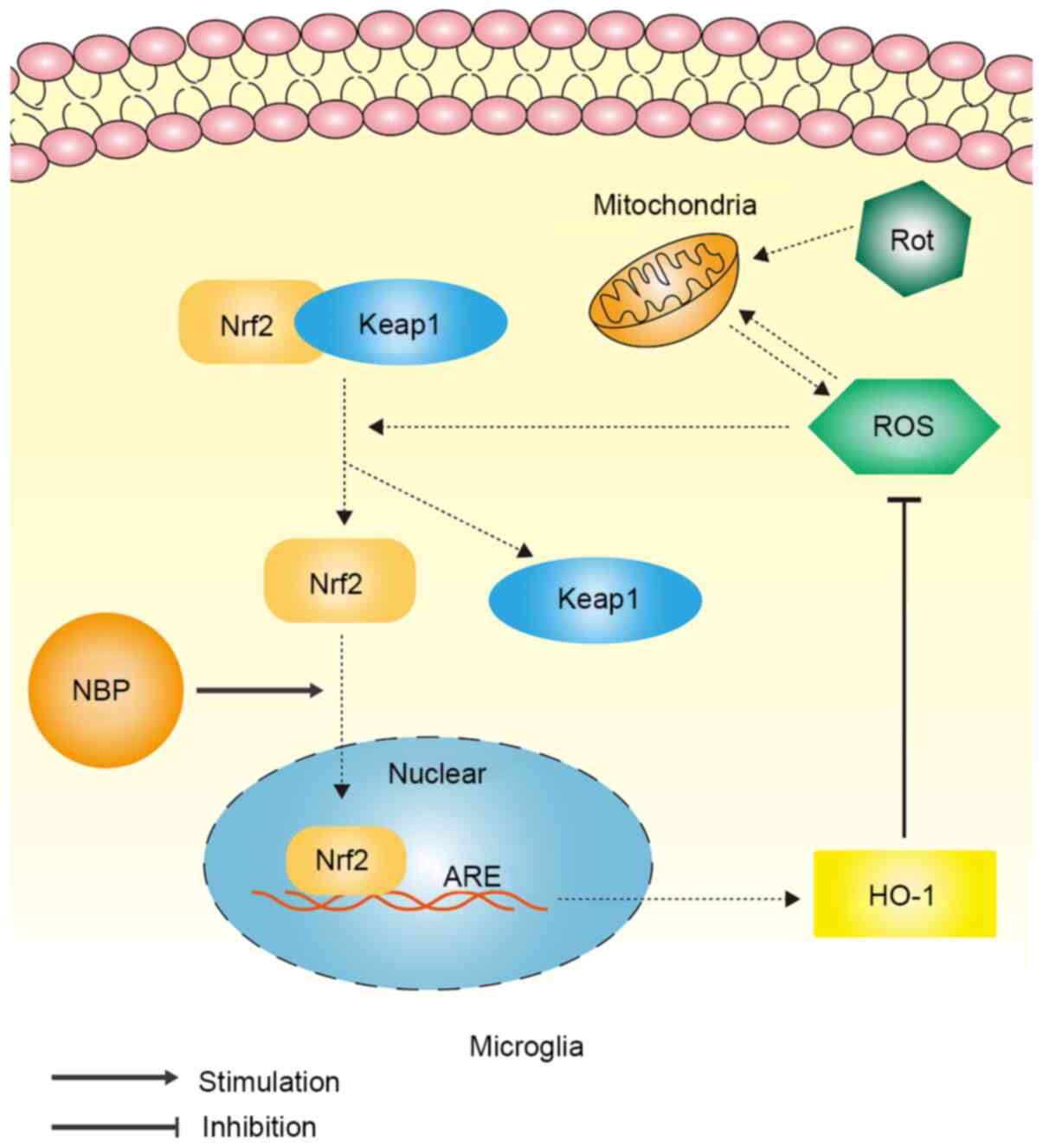
Dl‑butylphthalide inhibits rotenone‑induced oxidative stress in microglia via regulation of the Keap1/Nrf2/HO‑1 signaling pathway

Hypothetical model of rotenone-induced PD with possible therapeutic... | Download Scientific Diagram

Rotenone affects p53 transcriptional activity and apoptosis via targeting SIRT1 and H3K9 acetylation in SH‐SY5Y cells - Feng - 2015 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library
Transcriptome Analysis of a Rotenone Model of Parkinsonism Reveals Complex I-Tied and -Untied Toxicity Mechanisms Common to Neurodegenerative Diseases






![PDF] Mechanism of Toxicity in Rotenone Models of Parkinson's Disease | Semantic Scholar PDF] Mechanism of Toxicity in Rotenone Models of Parkinson's Disease | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/d916b6a33a7f1df587093bc1b16b3002f796ad39/3-Figure1-1.png)

